在编写 Python 代码时,许多人习惯性地依赖 baidu 或 ChatGPT 查找函数,但频繁地在工具之间切换不仅费时费力,还会导致精力消耗。根据 Meyer、Evans 和 Rubinstein 教授的研究,每次“任务切换”都会让生产力下降多达 40%。而掌握常用的 Python 方法和函数,不仅能减少这种“脑力消耗”,还能大幅提升编程效率。
参考:《Multitasking: Switching costs》https://www.apa.org/topics/research/multitasking
接下来,将介绍编程中最常用的 10 个 Python 函数,并为每个函数提供简洁的示例,帮助你更好地理解其用法。
一:Print 函数
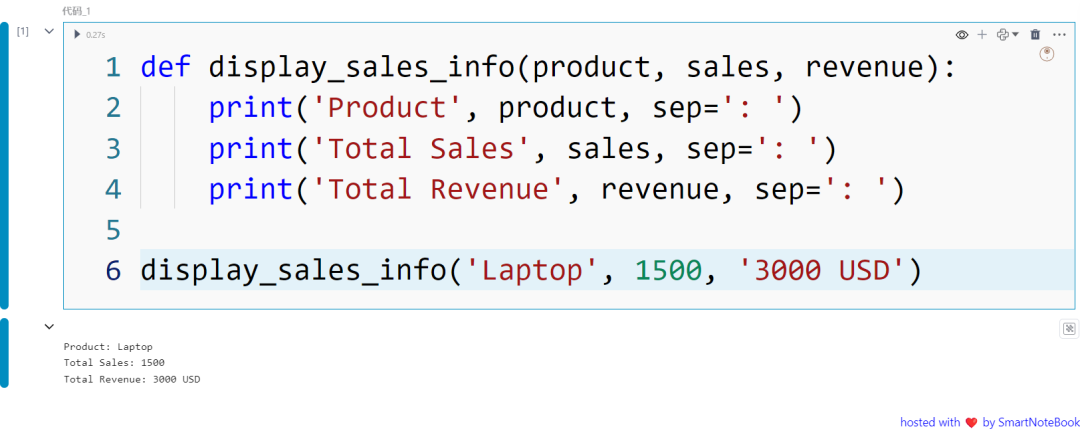
print() 函数是 Python 中最基本函数之一,是使用频率最高函数。在输出或debug调试是使用print()显示结果。也使用 sep 参数来进行一些灵活调整。
def display_sales_info(product, sales, revenue): print('Product', product, sep=': ') print('Total Sales', sales, sep=': ') print('Total Revenue', revenue, sep=': ')
display_sales_info('Laptop', 1500, '3000 USD')
二:help函数
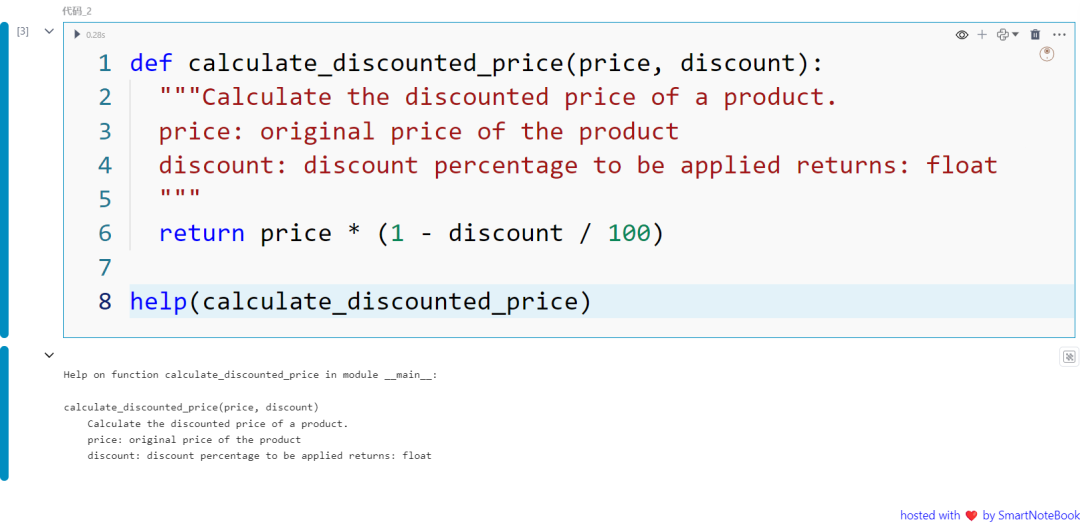
help() 函数在需要了解特定函数或模块的工作原理或帮助说明时非常有用。提供了指定函数或模块的文档说明。
def calculate_discounted_price(price, discount): """Calculate the discounted price of a product. price: original price of the product discount: discount percentage to be applied returns: float """ return price * (1 - discount / 100)
help(calculate_discounted_price)
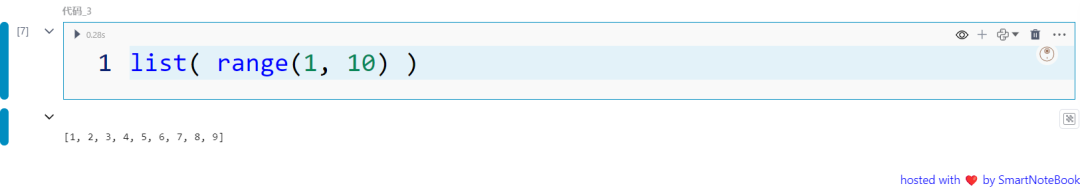
三:range 函数
range() 函数生成一个数字序列,非常适合在循环中进行迭代操作。
四:map 函数
map() 函数将指定的函数应用于输入列表中的所有元素。
def apply_discount(prices, discount): return list(map(lambda x: x * (1 - discount / 100), prices))
print(apply_discount([100, 200, 300, 400, 500], 10))

五:filter函数
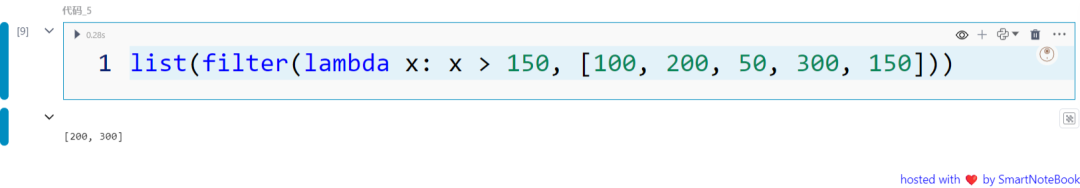
filter() 函数从可迭代对象中构建一个迭代器,返回满足函数条件为真的元素。
list(filter(lambda x: x > 150, [100, 200, 50, 300, 150]))
六:sorted 函数
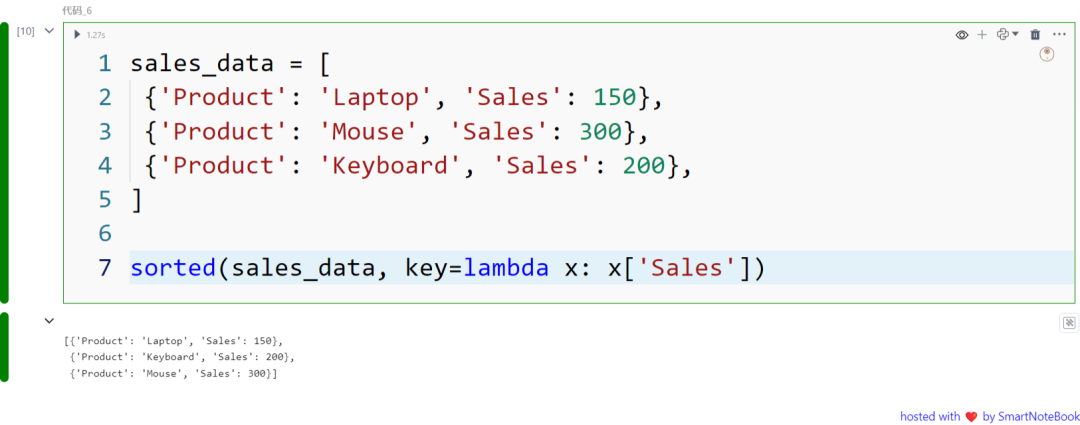
sorted() 函数从可迭代对象中返回一个排序后的列表。可以通过设置 reverse=True 来将排序顺序反转。
sales_data = [ {'Product': 'Laptop', 'Sales': 150}, {'Product': 'Mouse', 'Sales': 300}, {'Product': 'Keyboard', 'Sales': 200},]
sorted(sales_data, key=lambda x: x['Sales'])
七:enumerate 函数
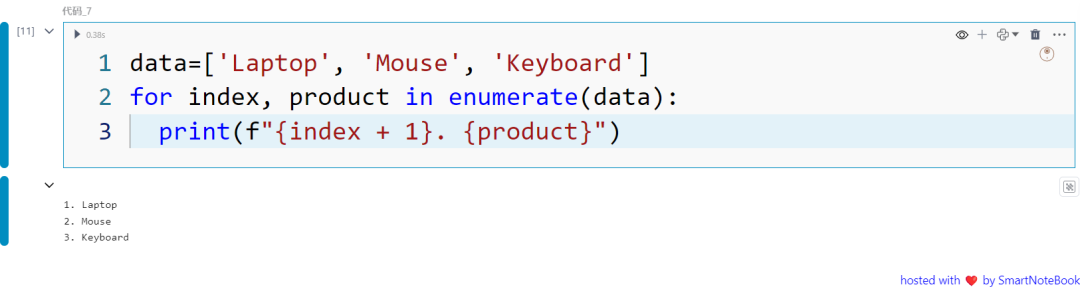
enumerate() 函数为可迭代对象添加一个计数器,并以枚举对象的形式返回。
data=['Laptop', 'Mouse', 'Keyboard']for index, product in enumerate(data): print(f"{index + 1}. {product}")
八:zip 函数
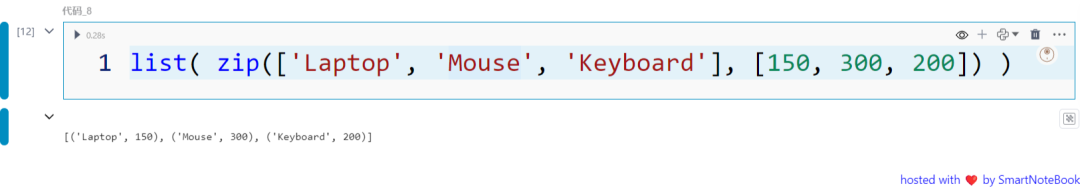
zip() 函数返回一个由元组组成的迭代器,每个元组将传入的多个迭代器中的第一个元素配对在一起,接着将每个迭代器的第二个元素配对在一起,依此类推。
list( zip(['Laptop', 'Mouse', 'Keyboard'], [150, 300, 200]) )
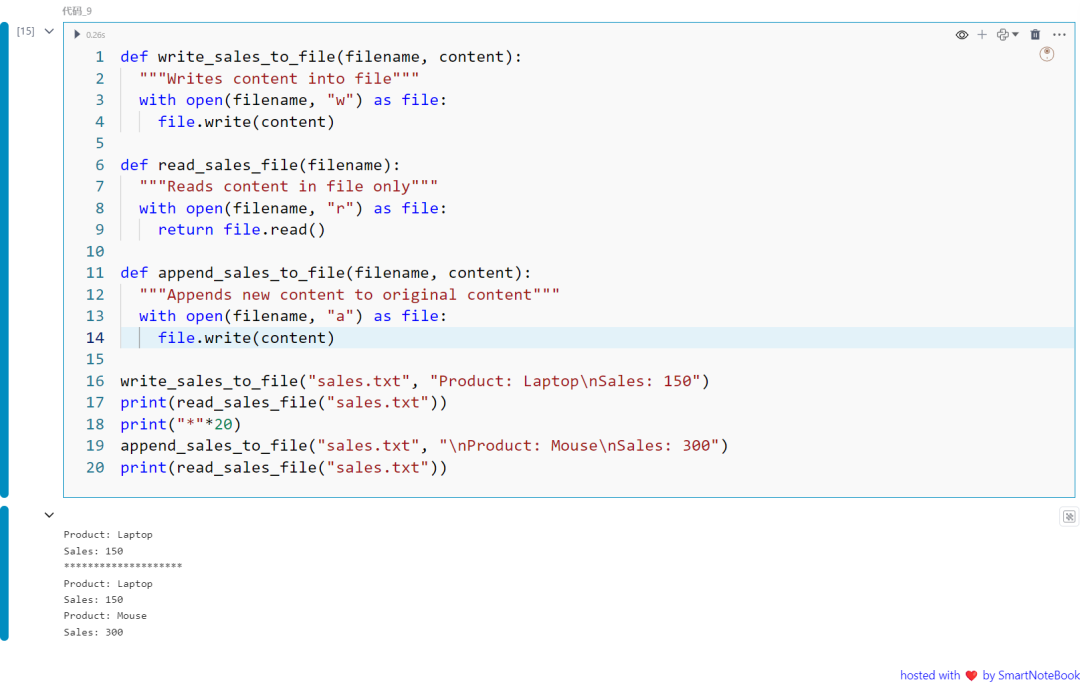
九:open 函数
open() 函数用于打开文件,返回一个文件对象,允许你对文件进行读取或写入操作。
def write_sales_to_file(filename, content): """Writes content into file""" with open(filename, "w") as file: file.write(content)
def read_sales_file(filename): """Reads content in file only""" with open(filename, "r") as file: return file.read()
def append_sales_to_file(filename, content): """Appends new content to original content""" with open(filename, "a") as file: file.write(content)
write_sales_to_file("sales.txt", "Product: Laptop\nSales: 150")print(read_sales_file("sales.txt"))print("*"*20)append_sales_to_file("sales.txt", "\nProduct: Mouse\nSales: 300")print(read_sales_file("sales.txt"))
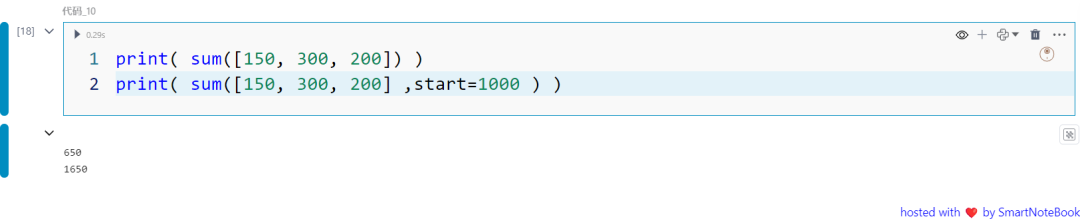
十:sum函数
sum() 函数从左到右对可迭代对象中的元素求和,并返回总和。你还可以设置 start 参数,在总和的基础上加上一个指定的数字。
print( sum([150, 300, 200]) )print( sum([150, 300, 200] ,start=1000 ) )
掌握这些函数后,可以无需频繁地在baidu和ChatGPT 之间切换,这不仅节省了时间,还能避免生产力的损失。将这些函数无缝集成到您的工作流程中,让您能够以闪电般的速度编写数据科学脚本。