
Python是一种多才多艺、被广泛使用的编程语言,拥有大量的库和框架。总结了近60个常用或较少人知晓的Python技巧的代码片段,每一个都能够为您的编程工具箱增添新的维度。从优化数据结构到简化算法,提高可读性到提升性能,这些代码片段不仅仅是代码 —— 它们是解锁Python全部潜力的关键。
1.for/while循环中的else子句
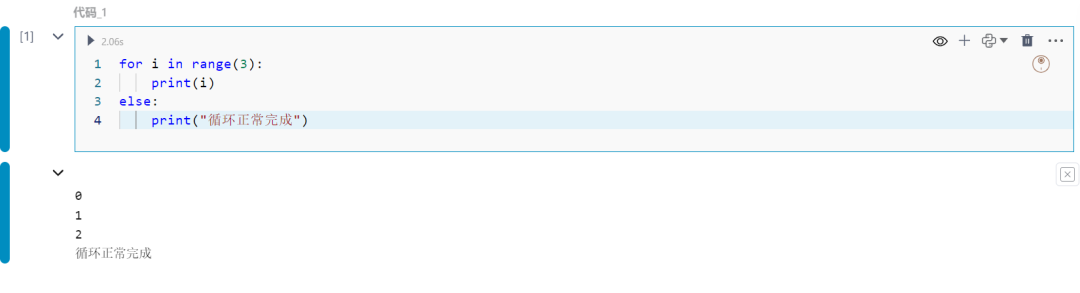
可以在for或while循环中使用else块。如果循环正常完成(没有遇到break语句),则会运行该块。
for i in range(3): print(i)else: print("循环正常完成")
2.enumerate函数
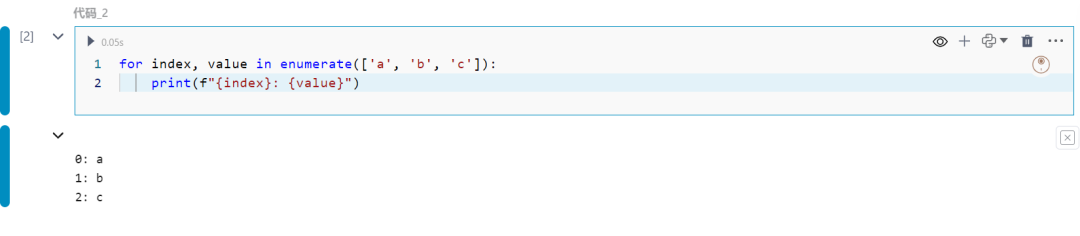
此函数向可迭代对象添加计数器并返回。
for index, value in enumerate(['a', 'b', 'c']): print(f"{index}: {value}")
3.带有if子句的列表推导式
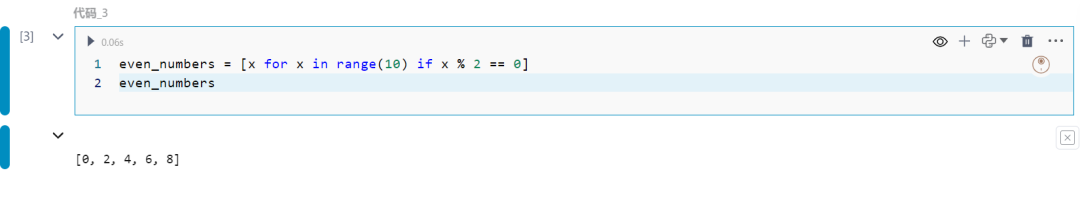
可以在列表推导式中if语句及过滤item。
even_numbers = [x for x in range(10) if x % 2 == 0]even_numbers
4.getattr函数
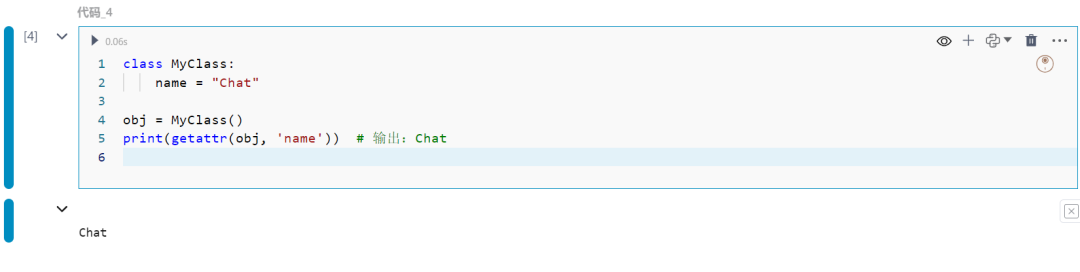
动态获取对象的属性。
class MyClass: name = "Chat"
obj = MyClass()print(getattr(obj, 'name'))
5.setattr函数
动态设置对象的属性。
setattr(obj, 'name', 'Chat1')print(obj.name)
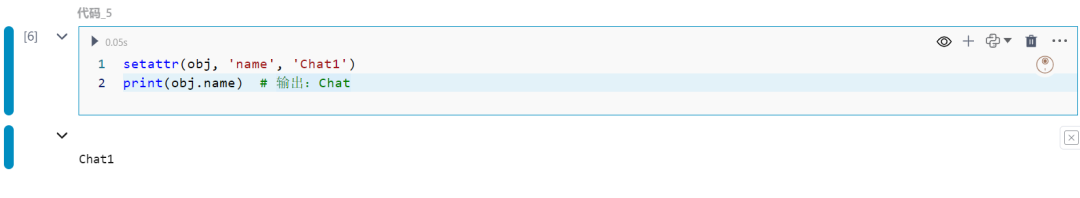
6.函数参数解包
可以使用*将列表或元组解包为函数参数。
def func(a, b, c): print(a, b, c)
args = [1, 2, 3]func(*args)
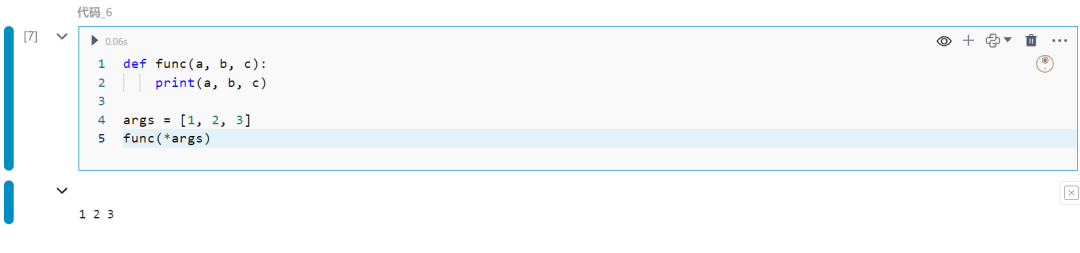
7.函数参数中的字典解包
使用**将字典解包为关键字参数。
def func(a=0, b=0): print(a, b)
kwargs = {'a': 1, 'b': 2}func(**kwargs)
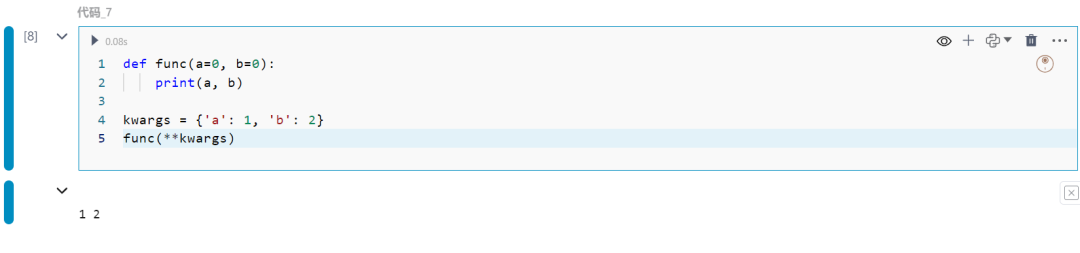
8.zip函数
将多个可迭代对象合并为一个。
names = ['Alice', 'Bob', 'Charlie']ages = [25, 30, 35]for name, age in zip(names, ages): print(f"{name} is {age} years old")
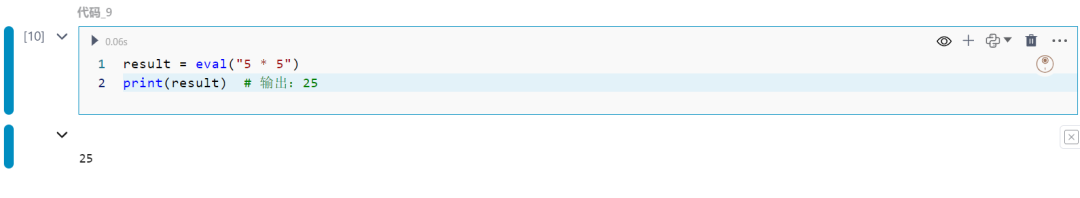
9.eval函数
将字符串作为Python表达式进行评估。
result = eval("5 * 5")print(result)
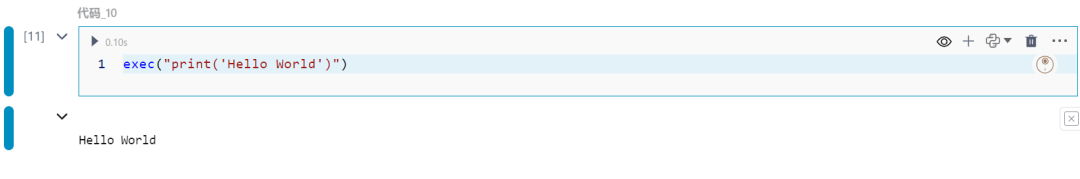
10.exec函数
执行动态创建的Python代码。
exec("print('Hello World')")
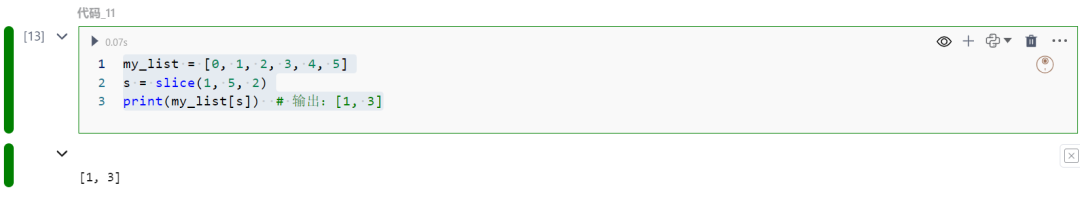
11.slice对象
为切片操作创建slice对象。
my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]s = slice(1, 5, 2)print(my_list[s])
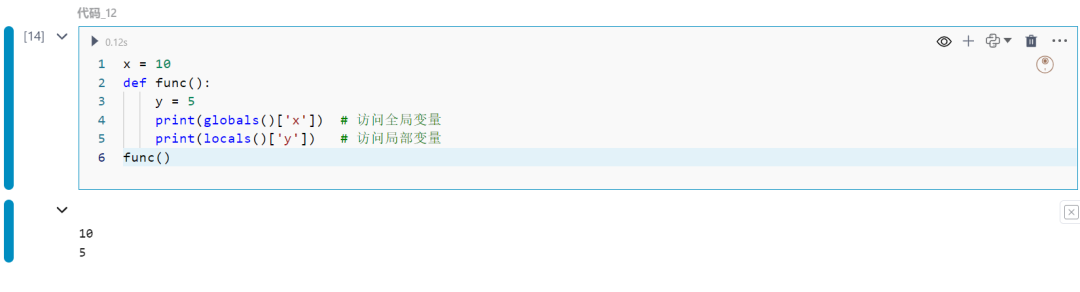
12.globals和locals函数
访问全局和局部符号表。
x = 10def func(): y = 5 print(globals()['x']) print(locals()['y']) func()
13.reversed函数
反转任何序列。
for i in reversed(range(5)): print(i)
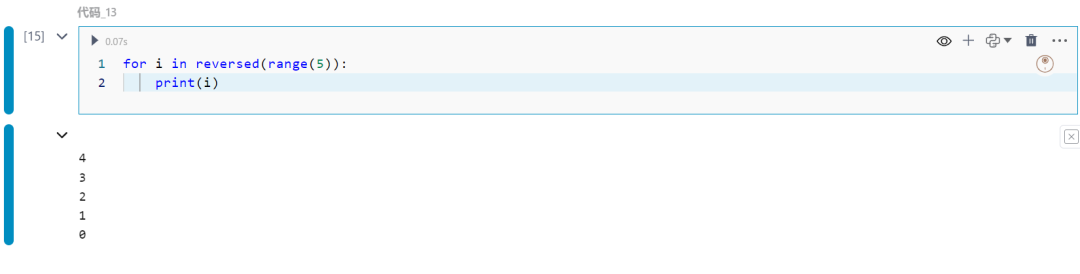
14.any和all函数
检查可迭代对象中是否有任何或所有元素为真。
print(any([False, True, False])) print(all([True, True, True]))
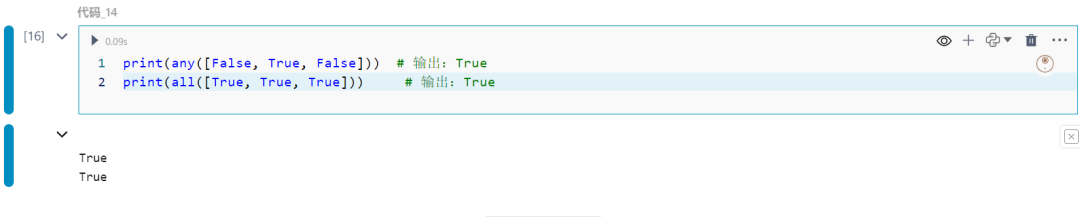
15.collections模块中的defaultdict
为缺失的键提供默认值。
from collections import defaultdictd = defaultdict(int)d['key'] += 1print(d['key'])
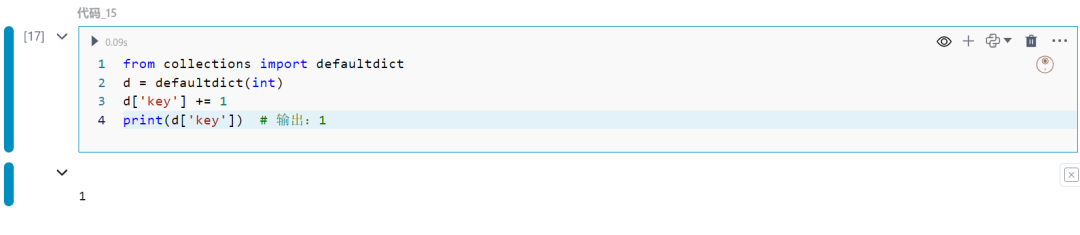
16.collections模块中的Counter
计算可迭代对象中的项目数。
from collections import Counterc = Counter('hello')print(c) # 输出:Counter({'l': 2, 'h': 1, 'e': 1, 'o': 1})
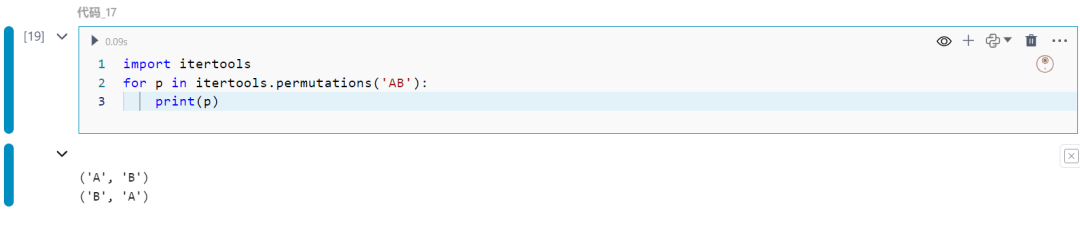
17.itertools模块
提供一组处理迭代器的工具。
import itertoolsfor p in itertools.permutations('AB'): print(p)
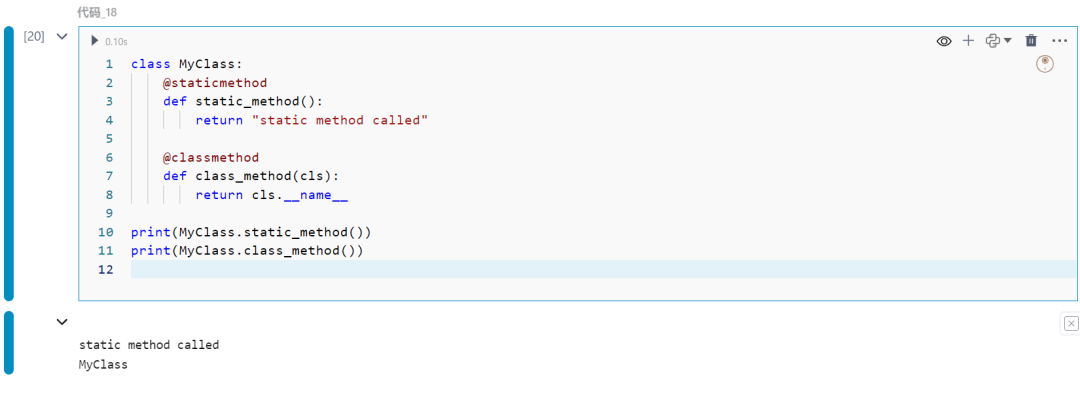
18.@staticmethod和@classmethod装饰器
定义不绑定到实例或类的方法。
class MyClass: @staticmethod def static_method(): return "static method called"
@classmethod def class_method(cls): return cls.__name__
print(MyClass.static_method())print(MyClass.class_method())
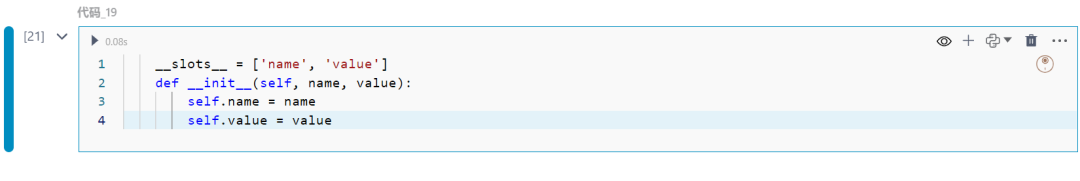
19.类中的__slots__
通过显式声明实例属性来优化内存使用。
class MyClass: __slots__ = ['name', 'value'] def __init__(self, name, value): self.name = name self.value = value
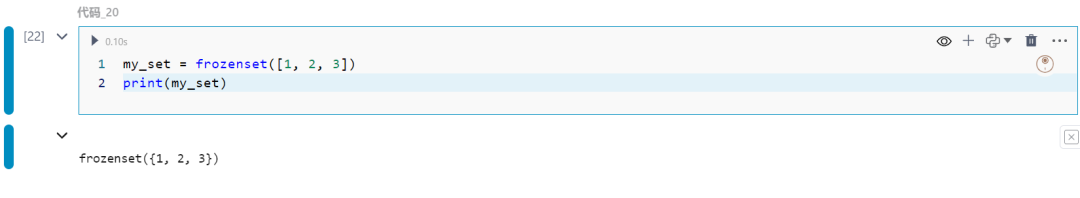
20.frozenset
不变的集合。
my_set = frozenset([1, 2, 3])print(my_set)
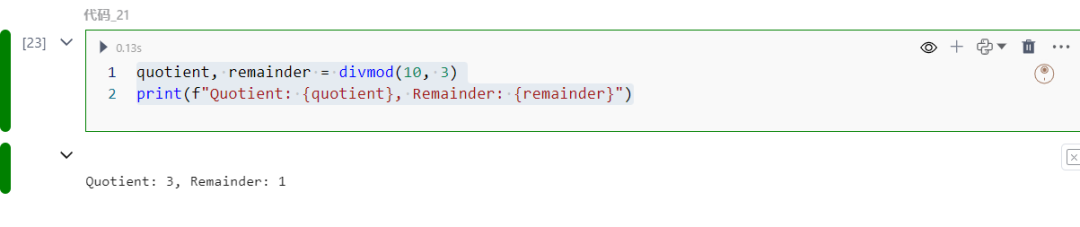
21.divmod函数
返回两个数字相除的商和余数。
quotient, remainder = divmod(10, 3)print(f"Quotient: {quotient}, Remainder: {remainder}")
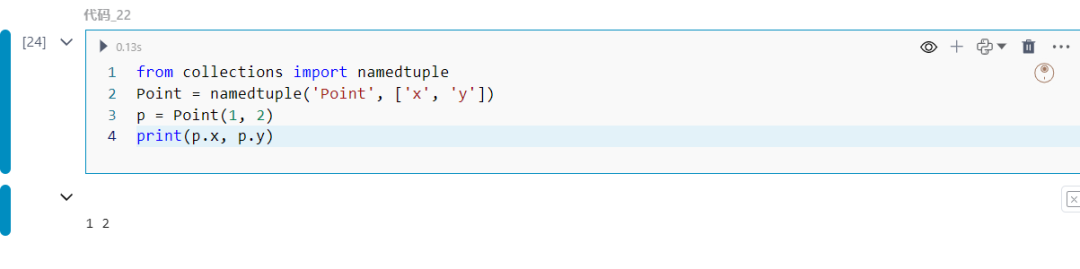
22.collections中的namedtuple
创建具有命名字段的类似元组的对象。
from collections import namedtuplePoint = namedtuple('Point', ['x', 'y'])p = Point(1, 2)print(p.x, p.y)
23.带有哨兵值的iter函数
创建一个在遇到哨兵值时停止的迭代器。
with open('file.txt', 'r') as f: for line in iter(lambda: f.readline().strip(), 'END'): print(line)

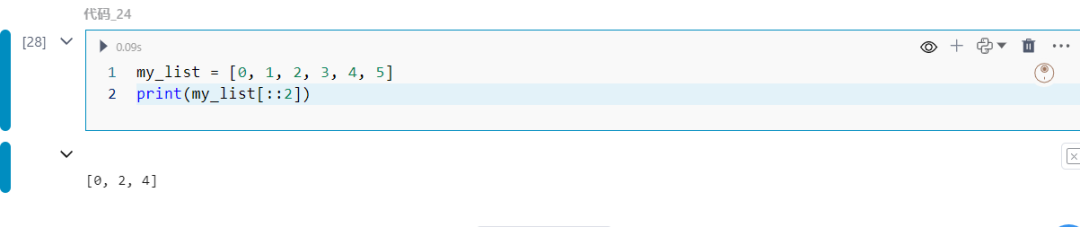
24.列表切片技巧
对列表进行高级切片的方法。
my_list = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5]print(my_list[::2])
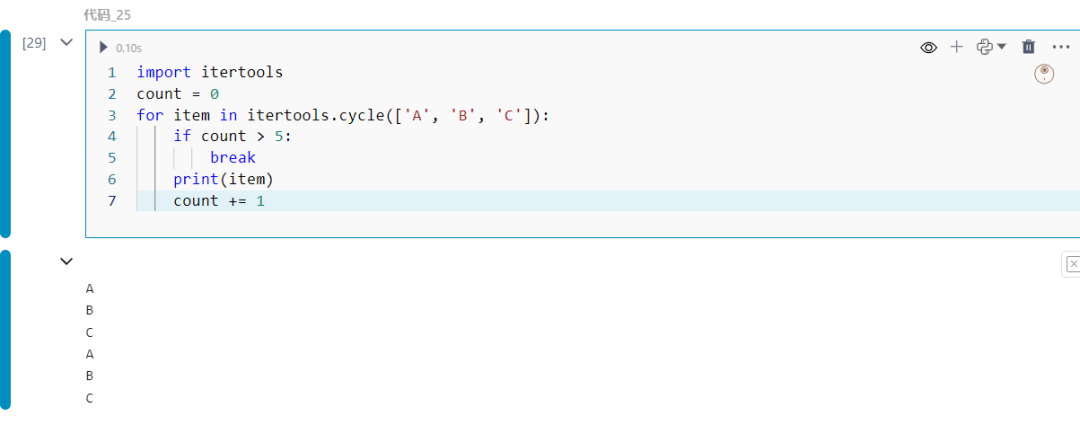
25.itertools.cycle
无限循环遍历可迭代对象。
import itertoolscount = 0for item in itertools.cycle(['A', 'B', 'C']): if count > 5: break print(item) count += 1
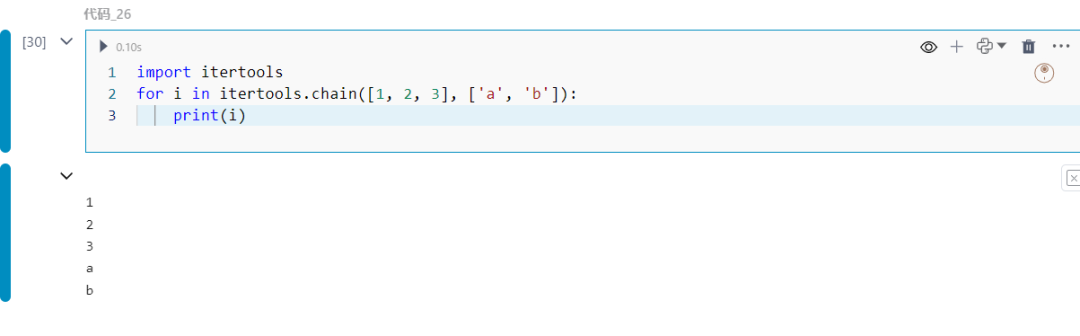
26.itertools.chain
链接多个可迭代对象。
import itertoolsfor i in itertools.chain([1, 2, 3], ['a', 'b']): print(i)
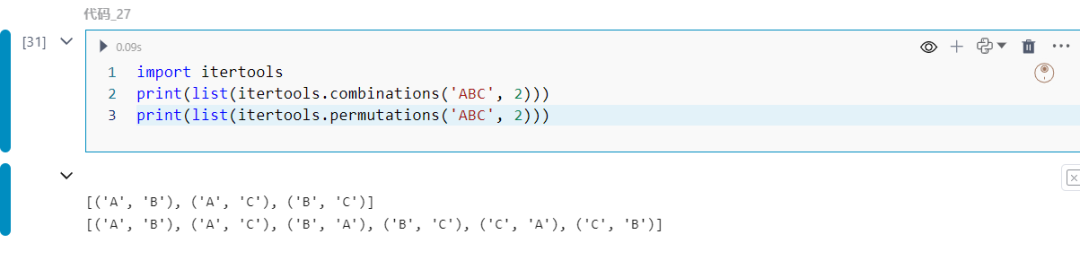
27.itertools.combinations和itertools.permutations
生成组合和排列。
import itertoolsprint(list(itertools.combinations('ABC', 2)))print(list(itertools.permutations('ABC', 2)))
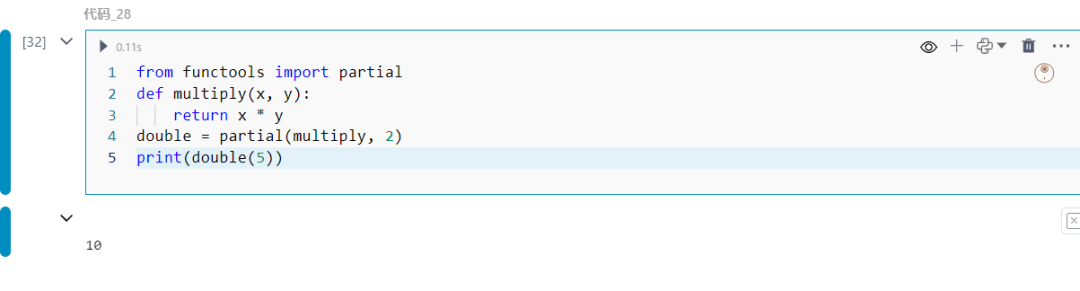
28.functools.partial
使用预填参数创建部分函数。
from functools import partialdef multiply(x, y): return x * ydouble = partial(multiply, 2)print(double(5))
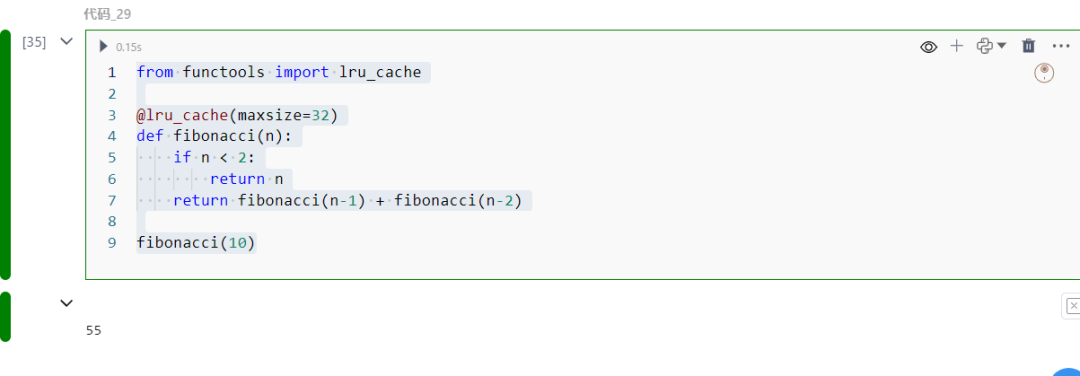
29.functools.lru_cache
缓存函数调用结果。
from functools import lru_cache
@lru_cache(maxsize=32)def fibonacci(n): if n < 2: return n return fibonacci(n-1) + fibonacci(n-2)
fibonacci(10)
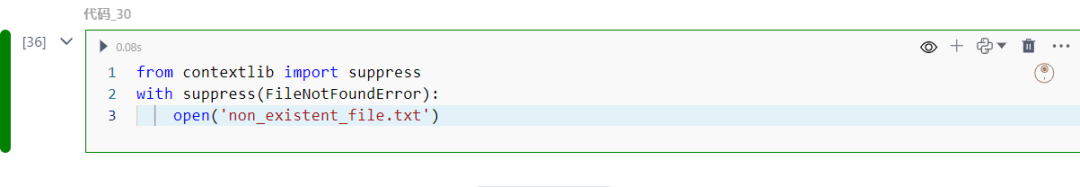
30.contextlib.suppress
忽略指定的异常。
from contextlib import suppresswith suppress(FileNotFoundError): open('non_existent_file.txt')
上述探索的30个Python隐藏功能和函数揭示了Python的深度和多样性;后续继续后30个技巧的探索。从使用较少人知晓的数据结构和itertools增强代码效率,通过上下文管理器和装饰器确保强大且更清洁的代码,到利用面向对象特性和内存管理的全部潜力,这些元素突显了Python满足各种编程需求的能力。