随机森林是机器学习中的一种集成学习方法,通过构建多个引入随机性的决策树来进行分类或回归预测,以提高模型的准确性和泛化能力。随机森林集成多个决策树,每个决策树基于自助采样数据集构建,分裂时随机选特征,最后投票(分类)或平均(回归)整合预测,提升准确性与泛化力。
集成学习(Ensemble Learning)是什么?集成学习是一种机器学习技术,它通过将多个学习器的预测结果进行组合,以提高整体的预测或分类性能。这些学习器可以是不同类型的,如决策树、支持向量机、神经网络等,也可以是相同类型的多个实例。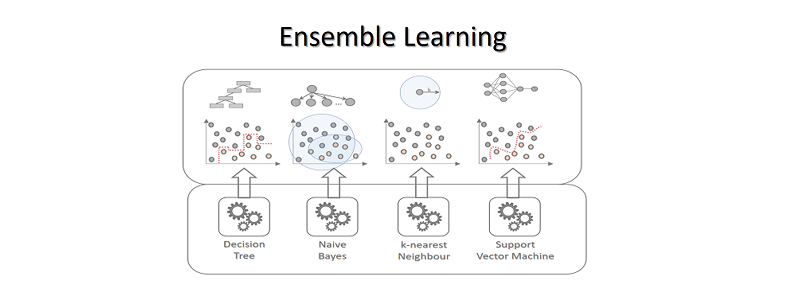
集成学习的实现方法有哪些?Bagging、Boosting和Stacking是三种常见的集成学习方法。Bagging并行训练多样本集基学习器,平均或投票预测降方差;Boosting串行纠正弱学习器错误,提升性能但易过拟合;Stacking则以基学习器预测为新特征,元模型组合得更优效果。Bagging:通过并行训练多个基于不同自助采样数据集的基学习器,并平均或投票其预测结果,以降低方差并提高模型的泛化能力。
Boosting:通过串行训练多个弱学习器,每个新模型都关注并纠正前一个模型的错误,逐步提高整体模型的性能,但可能导致过拟合。
Stacking:将多个基学习器的预测结果作为新的特征,训练一个元模型来组合这些预测,从而获得比单个模型更好的效果。
随机森林(Random Forest)是什么?随机森林是一种集成学习算法,它通过将多个决策树组合在一起形成一个强大的分类器或回归器。
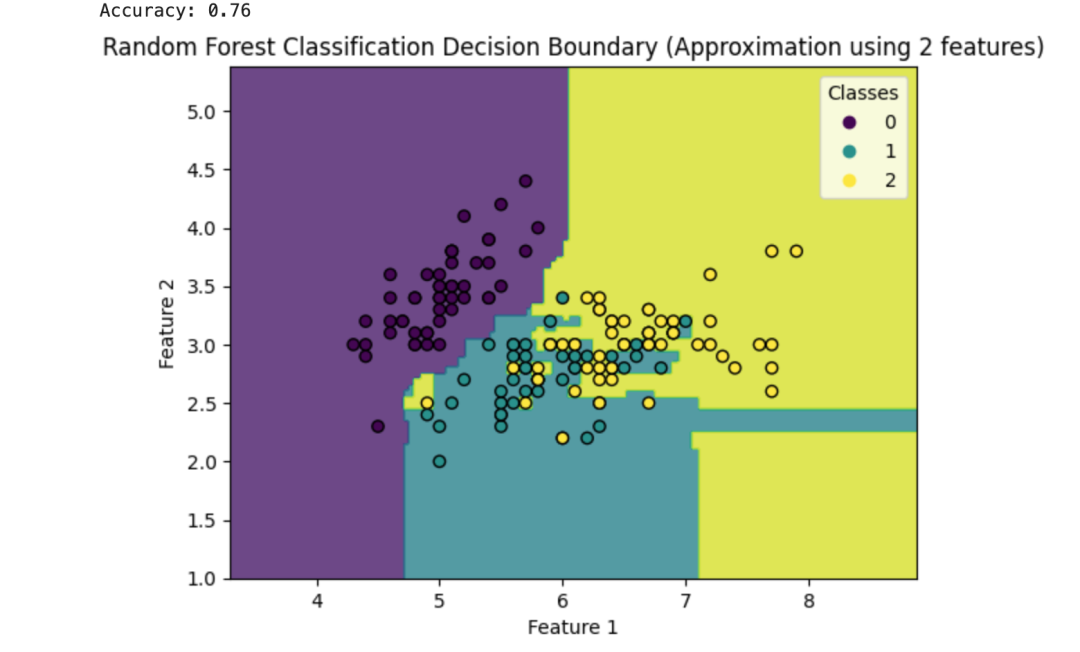
对于分类任务,随机森林取所有决策树的预测结果中占多数的类别作为最终预测结果。import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
data = load_iris()X = data.data[:, :2]y = data.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
clf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f'Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}')
h = .02 x_min, x_max = X[:, 0].min() - 1, X[:, 0].max() + 1y_min, y_max = X[:, 1].min() - 1, X[:, 1].max() + 1xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, h), np.arange(y_min, y_max, h))Z = clf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.8)scatter = plt.scatter(X[:, 0], X[:, 1], c=y, edgecolors='k', marker='o')plt.legend(*scatter.legend_elements(), title="Classes")plt.xlabel('Feature 1')plt.ylabel('Feature 2')plt.title('Random Forest Classification Decision Boundary (Approximation using 2 features)')plt.show()
对于回归任务,则取所有树预测结果的平均值作为最终预测结果。import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressorfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.datasets import load_diabetesfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
data = load_diabetes()X, y = data.data, data.target
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
reg = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=100, random_state=42)
reg.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = reg.predict(X_test)
mse = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)print(f'Mean Squared Error: {mse:.2f}')
plt.scatter(y_test, y_pred, edgecolors=(0, 0, 0))plt.plot([y_test.min(), y_test.max()], [y_test.min(), y_test.max()], 'k--', lw=4)plt.xlabel('Actual Values')plt.ylabel('Predicted Values')plt.title('Random Forest Regression: Actual vs Predicted')plt.show()

随机森林如何实现?随机森林是集成学习中Bagging方法的一种具体实现,通过
并行训练多个基于不同自助采样数据集的决策树,并组合其预测结果来提高整体模型的准确性和稳定性。
import numpy as npimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltfrom sklearn.datasets import load_irisfrom sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifierfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
iris = load_iris()X, y = iris.data, iris.target
feature_indices = [0, 1] X_vis = X[:, feature_indices]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X_vis, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
class RandomForest: def __init__(self, n_estimators=100, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, random_state=42): self.n_estimators = n_estimators self.max_depth = max_depth self.min_samples_split = min_samples_split self.random_state = random_state self.trees = [] np.random.seed(random_state)
def fit(self, X, y): for _ in range(self.n_estimators): indices = np.random.choice(X.shape[0], X.shape[0], replace=True) X_sample, y_sample = X[indices], y[indices]
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=self.max_depth, min_samples_split=self.min_samples_split, random_state=self.random_state) tree.fit(X_sample, y_sample) self.trees.append(tree)
def predict(self, X): tree_preds = np.array([tree.predict(X) for tree in self.trees])
majority_votes = np.apply_along_axis(lambda x: np.bincount(x).argmax(), axis=0, arr=tree_preds) return majority_votes
rf = RandomForest(n_estimators=100, max_depth=None, min_samples_split=2, random_state=42)rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = rf.predict(X_test)accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)print(f'Accuracy: {accuracy:.2f}')
x_min, x_max = X_vis[:, 0].min() - 1, X_vis[:, 0].max() + 1y_min, y_max = X_vis[:, 1].min() - 1, X_vis[:, 1].max() + 1xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.01), np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.01))
Z = rf.predict(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()])Z = Z.reshape(xx.shape)
plt.contourf(xx, yy, Z, alpha=0.3)plt.scatter(X_test[:, 0], X_test[:, 1], c=y_test, edgecolors='k', marker='o', cmap=plt.cm.Paired)plt.xlabel(iris.feature_names[feature_indices[0]])
plt.ylabel(iris.feature_names[feature_indices[1]])plt.title('Random Forest Decision Boundaries (2 features)')plt.show()
