
Advanced Manufacturing News
ISSN: 2959-3263 (Print)
ISSN: 2959-3271 (Online)
Advanced Manufacturing(《先进制造》)期刊创建于2022年1月1日,ISSN号 2959-3271,主编由美国普渡大学Yung C. Shin教授(H-index 75)担任,编委委员由西北工业大学副校长、中国科学院院士张卫红教授(H-index 63)等人担任,编委会平均H-index为60。目前编委会42人,涵盖22个国家,29所国内外知名高校、实验室、研究机构。《先进制造》专注于在先进制造领域发表原创性文章、观点、报告和评论,面向国际和国内,致力于打造先进制造国际化顶级期刊,与全世界学者一道共建学术生态圈。
期刊研究范围包括但不限于:
● 计算机辅助设计和计算机辅助制造(例如CAD/CAM、CAE)
● 用于建模、仿真和分析的高性能计算 (HPC)
● 制造系统,包括自动化、机器人、智能控制和监控系统
● 激光加工及应用、电加工、机械加工等先进制造技术
● 微纳制造
● 制造过程和系统的建模技术
● 3D打印(增材制造)
● 可持续绿色技术及过程
● 极端条件制造
● 先进制造材料
● 工业4.0
● 数字化制造

Professor Yung C. Shin
Purdue University, USA
A review on physics-informed machine learning for monitoring metal additive manufacturing process
Shoulan Yang, Shitong Peng∗, Jianan Guo, Fengtao Wang∗
Department of Mechanical Engineering, Shantou University, Shantou, 515063, China
Citation:Yang S, Peng S, Guo J, Wang F. A review on physics-informed machine learning for monitoring metal additive manufacturing process. Adv. Manuf. 2024(2):0008, https://doi.org/10.55092/am20240008.
DOI: 10.55092/am20240008
Abstract:
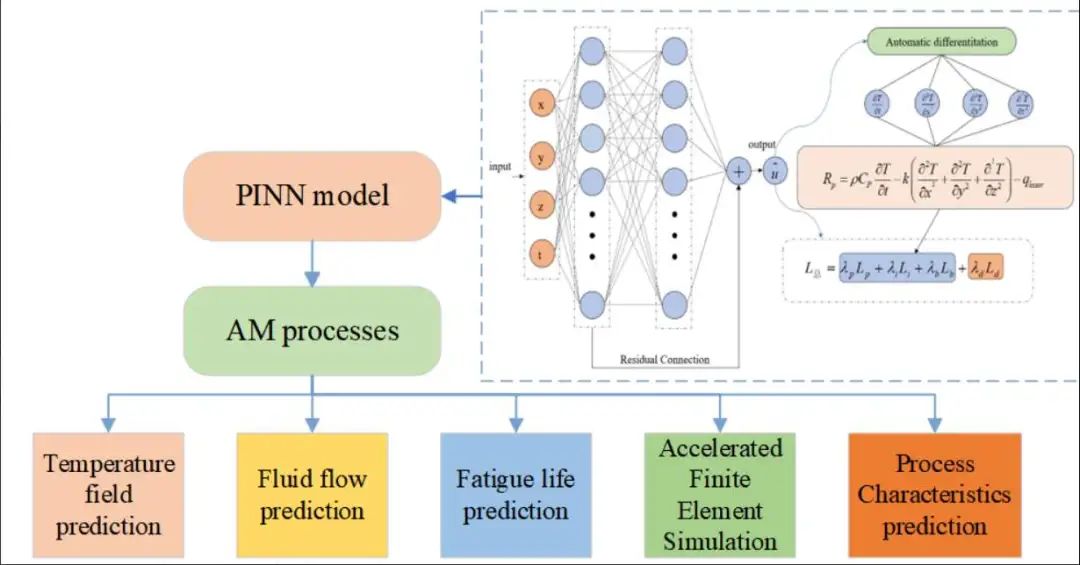
The traditional data-driven models and pure physics models have been widely employed in quality prediction for additive manufacturing (AM). However, data-driven models rely on a large amount of labeled data, while pure physics models suffer from lower computational efficiency and accuracy. The Physics-Informed Neural Network (PINN) model has emerged as a hybrid data-driven paradigm that imbues data-driven models with physical domain knowledge. To refrain from the inherent “black box” or inefficiency of AM process prediction or monitoring, this paper discusses the pros and cons of traditional data driven methods and pure physics models and further elaborates on the principles and architecture of the PINN model along with its applications in AM research. We review and analyze current state-of-the-art PINN applications to AM, focusing on temperature field prediction, fluid dynamics issues, fatigue life prediction, accelerated finite element simulation, and process characteristics prediction. The corresponding embedded physical knowledge, either integrated into loss function or data preprocessing, is also summarized for these applications. Based on this review, we identify the challenges of PINN and provide an outlook for further research of its AM applications.
Keywords: Data-driven models; physics models; additive manufacturing; physics-informed neural network

识别二维码,阅读原文
Preview:
1. Advanced Manufacturing 期刊官网:
https://www.elspub.com/journals/advanced-manufacturing/home
2. Advanced Manufacturing 编辑部邮箱:
advmanufact@elspub.com
3. 投稿链接:
https://jms.elspub.com/login











