
在市值排名前 10 的加密货币中,从纯粹的经济角度来看,你认为自 2017 年以来表现最好的加密货币是哪一种?
不管你信不信,币安自己的 BNB 实际上远远超过了其他所有加密货币。我编写了一个脚本来帮助我了解几种加密货币的历史表现,当我决定只加入前 10 名加密货币并看看表现最好的货币是哪个。在运行脚本之前,我很确定它可能将是 DOGE。所以我坐在这里,等待历史数据下载,以便我的脚本可以绘制一些加密图表。脚本运行完毕,结果出来了,感谢中本聪,这不是 DOGE。哦,等等,这更有趣——它是 BNB。自 2017 年以来,BNB 已上涨超过 20,000%。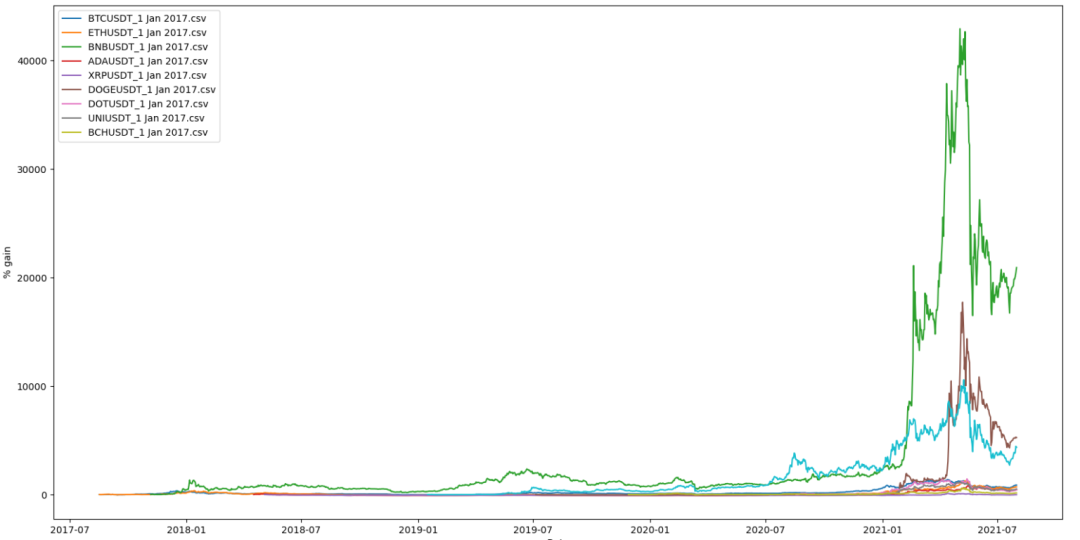
程序能够为你下载历史数据,并分析任意数量的币种。如果您想对任意数量的加密货币的收益百分比进行快速比较分析,这很方便。您所需要的只是一些 Python 知识。https://github.com/CyberPunkMetalHead/crypto-performance-tracker
首先创建一个文本文件并将其命名为coins.txt。在此文本文件中,放入一些您想要分析的币种名称。它们需要包含配对符号,并且每行必须是 1 个货币,不能有逗号:创建一个 binancedata.py 文件。我们将使用此文件轮询 Binance API 以获取我们需要的金融数据。由于我们使用的是开放端口,因此不需要 API 密钥和密码。让我们导入一些依赖项并定义一个空的 Binance 客户端:# needed for the binance API and websockets
from binance.client import Client
import csv
import os
import time
from datetime import date, datetime
client = Client()
现在让我们编写一个函数来从我们的coins.txt文件中打开和读取货币:def get_coins():
with open('coins.txt', 'r') as f:
coins = f.readlines()
coins = [coin.strip('\n') for coin in coins]
return coins
此文件中的最后一个函数将为我们获取历史数据并以 CSV 格式保存:
def get_historical_data(coin, since, kline_interval):
"""
Args example:
coin = 'BTCUSDT'
since = '1 Jan 2021'
kline_interval = Client.KLINE_INTERVAL_1MINUTE
"""
if os.path.isfile(f'data/{coin}_{since}.csv'):
print('Datafile already exists, loading file...')
else:
print(f'Fetching historical data for {coin}, this may take a few minutes...')
start_time = time.perf_counter()
data = client.get_historical_klines(coin, kline_interval, since)
data = [item[0:5] for item in data]
# field names
fields = ['timstamp', 'high', 'low', 'open', 'close']
# save the data
with open(f'data/{coin}_{since}.csv', 'w', newline='') as f:
# using csv.writer method from CSV package
write = csv.writer(f)
write.writerow(fields)
write.writerows(data)
end_time = time.perf_counter()
# calculate how long it took to produce the file
time_elapsed = round(end_time - start_time)
print(f'Historical data for {coin} saved as {coin}_{since}.csv. Time elapsed: {time_elapsed} seconds')
return f'{coin}_{since}.csv'
此函数还将检查文件是否已经存在,如果存在它不会再次下载。该函数接受 3 个参数:coin、since 和 kline_interval。检查函数下方的注释,了解我们将传递给这些参数的正确格式。保存文件,现在是创建我们的主要执行文件的时候了,我们将把这个文件的内容导入到其中。继续创建一个 main.py 文件并安装以下依赖项:
from binancedata import *
import threading
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.cbook as cbook
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# needed for the binance API and websockets
from binance.client import Client
import csv
import os
import time
from datetime import datetime, date
让我们开始一些线程。该脚本是为了一次下载多个数据文件,所以为了避免等待一次下载每个历史数据文件,我们将使用线程并下载这些文件,如下所示:threads = []
coins = get_coins()
for coin in coins:
t = threading.Thread(target=get_historical_data, args=(coin, '1 Jan 2017', Client.KLINE_INTERVAL_1DAY) ) #'get_historical_data('ETHUSDT', '1 Jan 2021', Client.KLINE_INTERVAL_1MINUTE)
t
.start()
threads.append(t)
[thread.join() for thread in threads]
现在我们需要一个函数来返回我们下载的所有数据文件的文件名:def get_all_filenames():
return [get_historical_data(coin, '1 Jan 2017', Client.KLINE_INTERVAL_1DAY) for coin in coins]
最后,我们将定义主要函数,我们将在其中绘制这些数据并运行脚本:def main():
historical_data = get_all_filenames()
for file in historical_data:
data = pd.read_csv(f'data/{file}')
rolling_percentage = data['close']
rolling_percentage = [(item - rolling_percentage[0]) / rolling_percentage[0]*100 for item in rolling_percentage ]
timestamp = data['timstamp']
timestamp = [datetime.fromtimestamp(item/1000) for item in timestamp]
plt.legend()
plt.plot(timestamp, rolling_percentage, label=file)
plt.xlabel("Date")
plt.ylabel("% gain")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
现在剩下要做的就是在脚本目录中创建一个空文件夹并将其命名为 data。大功告成,您现在可以分析您想要的所有代币的历史收益。

点击下方阅读原文加入社区会员